GATE 1997
Question 1 |
The probability that it will rain today is 0.5. The probability that it will rain tomorrow is 0.6. The probability that it will rain either today or tomorrow is 0.7. What is the probability that it will rain today and tomorrow?
0.3 | |
0.25 | |
0.35 | |
0.4 |
P(Tomorrow) = 0.6
P(T∪To) = 0.7
P(T∩To) = P(T) + P(To) - P(T∪To)
= 0.5 + 0.6 - 0.07
= 1.1 - 0.7
= 0.4
Question 2 |
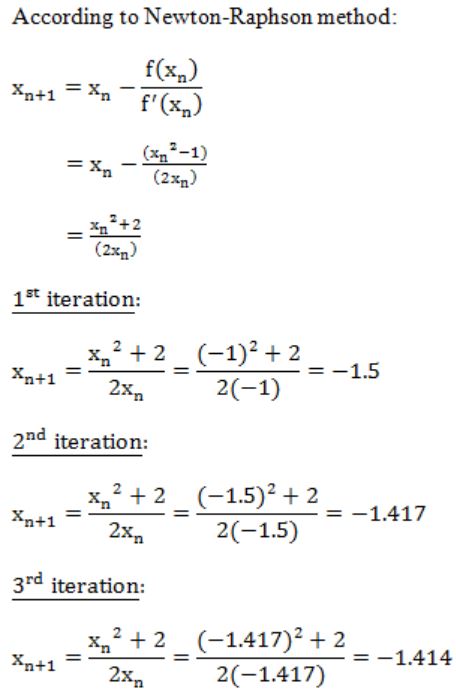
The Newton-Raphson method is used to find the root of the equation x2 - 2 = 0. If the iterations are started from -1, the iterations will
converge to -1 | |
converge to √2 | |
converge to - √2 | |
not converge |
Question 3 |
The determinant of the matrix is  is:
is:
11 | |
-48 | |
0 | |
-24 |
Question 4 |
The concatenation of two lists is to be performed in O(1) time. Which of the following implementations of a list should be used?
Singly linked list | |
Doubly linked list | |
Circular doubly linked list | |
Array implementation of list |
Question 5 |
The correct matching for the following pairs is
(A) All pairs shortest path (1) Greedy (B) Quick Sort (2) Depth-First search (C) Minimum weight spanning tree (3) Dynamic Programming (D) Connected Components (4) Divide and and Conquer
A – 2 B – 4 C – 1 D – 3 | |
A – 3 B – 4 C – 1 D – 2 | |
A – 3 B – 4 C – 2 D – 1 | |
A – 4 B – 1 C – 2 D – 3 |
Quick sort - Divide and Conquer
Minimum weight Spanning tree - Greedy
Connected components - Depth-First search
Question 6 |
In the following grammar
X ::= X ⊕ Y/Y
Y ::= Z * Y/Z
Z ::= id
Which of the following is true?
‘⊕’ is left associative while ‘*’ is right associative | |
Both ‘⊕’ and ‘*’ is left associative | |
‘⊕’ is right associative while ‘*’ is left associative | |
None of the above |
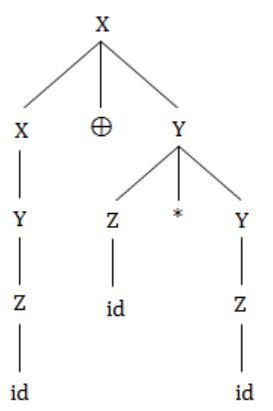
⊕ is left associative.
* is right associative.
Question 7 |
Which of the following is essential for converting an infix expression to the postfix from efficiently?
An operator stack | |
An operand stack | |
An operand stack and an operator stack | |
A parse tree |
An operand stack ⇒ Postfix to Prefix
Operator & operand stack ⇒ We don't use two stacks
Parse tree ⇒ No use
Question 8 |
A language L allows declaration of arrays whose sizes are not known during compilation. It is required to make efficient use of memory. Which of the following is true?
A compiler using static memory allocation can be written for L | |
A compiler cannot be written for L; an interpreter must be used | |
A compiler using dynamic memory allocation can be written for L | |
None of the above |
Question 9 |
The conditional expansion facility of macro processor is provided to
test a condition during the execution of the expanded program | |
to expand certain model statements depending upon the value of a condition during the execution of the expanded program | |
to implement recursion | |
to expand certain model statements depending upon the value of a condition during the process of macro expansion |
Question 10 |
Heap allocation is required for languages
that support recursion | |
that support dynamic data structures | |
that use dynamic scope rules | |
None of the above |
Question 11 |
Let * be defined as x * y = x' + y. Let z = x * y. Value of z * x is
x'+y | |
x | |
0 | |
1 |
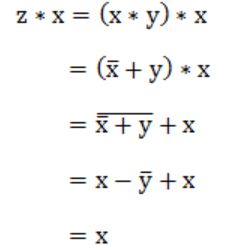
Question 12 |
RST 7.5 interrupt in 8085 microprocessor executes the interrupt service routine from interrupt vector location
0000H | |
0075H | |
003CH | |
0034H |
→ 60 in hexa decimal is 003CH.
Question 13 |
Purpose of a start bit in RS 232 serial communication protocol is
to synchronize receiver for receiving every byte | |
to synchronize receiver for receiving a sequence of bytes | |
a parity bit | |
to synchronize receiver for receiving the last byte |
Question 14 |
The correct matching for the following pairs is
(A) DMA I/O (1) High speed RAM (B) Cache (2) Disk (C) Interrupt I/O (3) Printer (D) Condition Code Register (4) ALU
A – 4 B – 3 C – 1 D – 2 | |
A – 2 B – 1 C – 3 D – 4
| |
A – 4 B – 3 C – 2 D – 1 | |
A – 2 B – 3 C – 4 D – 1 |
Cache → High speed RAM
Interrupt I/O → Printer
Condition code register → ALU
Question 15 |
An N-bit carry look ahead adder, where N is a multiple of 4, employs ICs 74181 (4 bit ALU) and 74182 (4 bit carry look ahead generator).
The minimum addition time using the best architecture for this adder is
proportional to N | |
proportional to log N | |
a constant | |
None of the above |
Question 16 |
Let (Z,*) be an algebraic structure, where Z is the set of integers and the operation * is defined by n*m = maximum (n,m). which of the following statements is true for (Z,*)?
(Z,*) is a monoid | |
(Z,*) is an Abelian group | |
(Z,*) is a group | |
None of the above |
Monoid - Closed, Associative and has an identity
Group - Monoid with inverse
Abelian group - Group with commutative property
Go through with given:
Closure: Yes.
(m*n = max(m,n)) output is either m or n whichever is maximum since m,n belongs z. The result of the binary operation also belongs to z. So given is satisfying closure property.
Associative: Yes.
The output is max among the elements and it is associative.
Identity: No.
We don't have single unique element for all the elements which is less than all the elements.
Given one is semigroup only.
Question 17 |
Which of the following propositions is a tautology?
(p ∨ q) → p | |
p ∨ (q → p) | |
p ∨ (p → q) | |
p → (p → q) |

Question 18 |
In a lattice defined by the Hasse diagram given in following figure, how many complements does the element 'e' have?
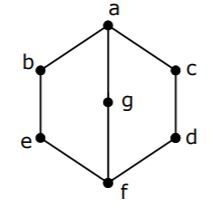
2 | |
3 | |
0 | |
1 |
No. of complements = 3
e∨g = a and e∧g = f
e∨c = a and e∧c = f
e∨d = a and e∧d = f
